Adiponectin: The Hidden Hormone That Makes Weight Loss Safer, Easier, and More Sustainable
Published on January 7, 2026

Free Resource
The 7-Day Adiponectin Reset
Support insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and improve metabolic flexibility A realistic reset focused on habits that improve how your body handles food — not restriction, guilt, or extremes.
Download the guide
Download the Visceral Fat → Adiponectin Explainer
A one-page visual guide that makes this connection clear
Most weight-loss advice focuses on what to eat or how much to eat.
Very little talks about how your body responds to food.
That response — how efficiently you burn fat, manage blood sugar, and preserve muscle — is strongly influenced by a hormone most people have never heard of:
Adiponectin.
Understanding adiponectin helps explain:
- Why weight loss feels effortless for some people and brutal for others
- Why crash dieting often backfires
- Why “doing everything right” still doesn’t always lead to fat loss
- How you can lose fat without sacrificing muscle
This is one of the most overlooked keys to sustainable weight loss.
What Is Adiponectin (in plain language)?
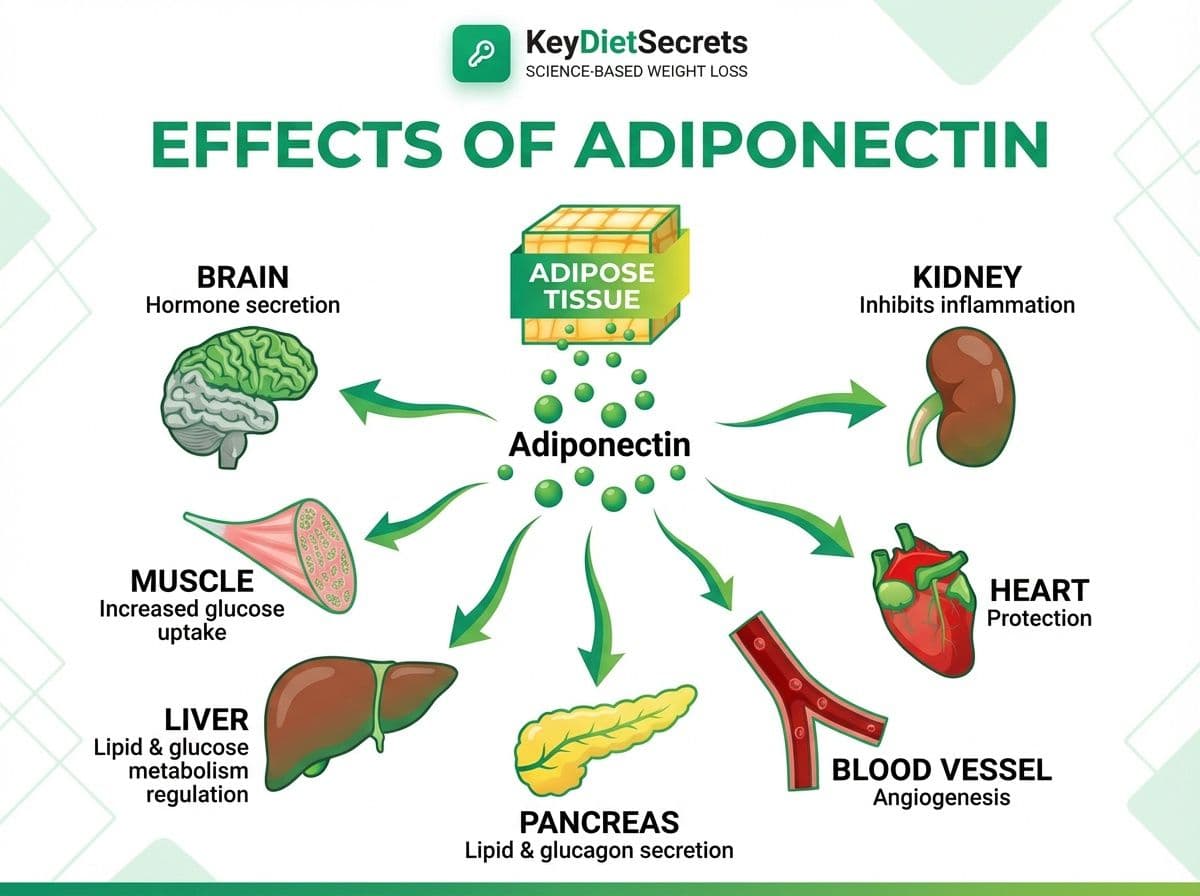
Adiponectin is a hormone released primarily by fat tissue that helps regulate how your body uses fat and glucose for energy.
When adiponectin signaling is healthy, your body tends to:
- Respond better to insulin
- Burn fat more efficiently
- Store less fat in harmful visceral areas
- Experience lower levels of chronic inflammation
Here’s the counterintuitive part:
As metabolic health declines — especially with increased visceral fat — adiponectin levels often drop, even though fat mass increases.
This is why adiponectin is better thought of as a metabolic health signal, not a “fat hormone.”
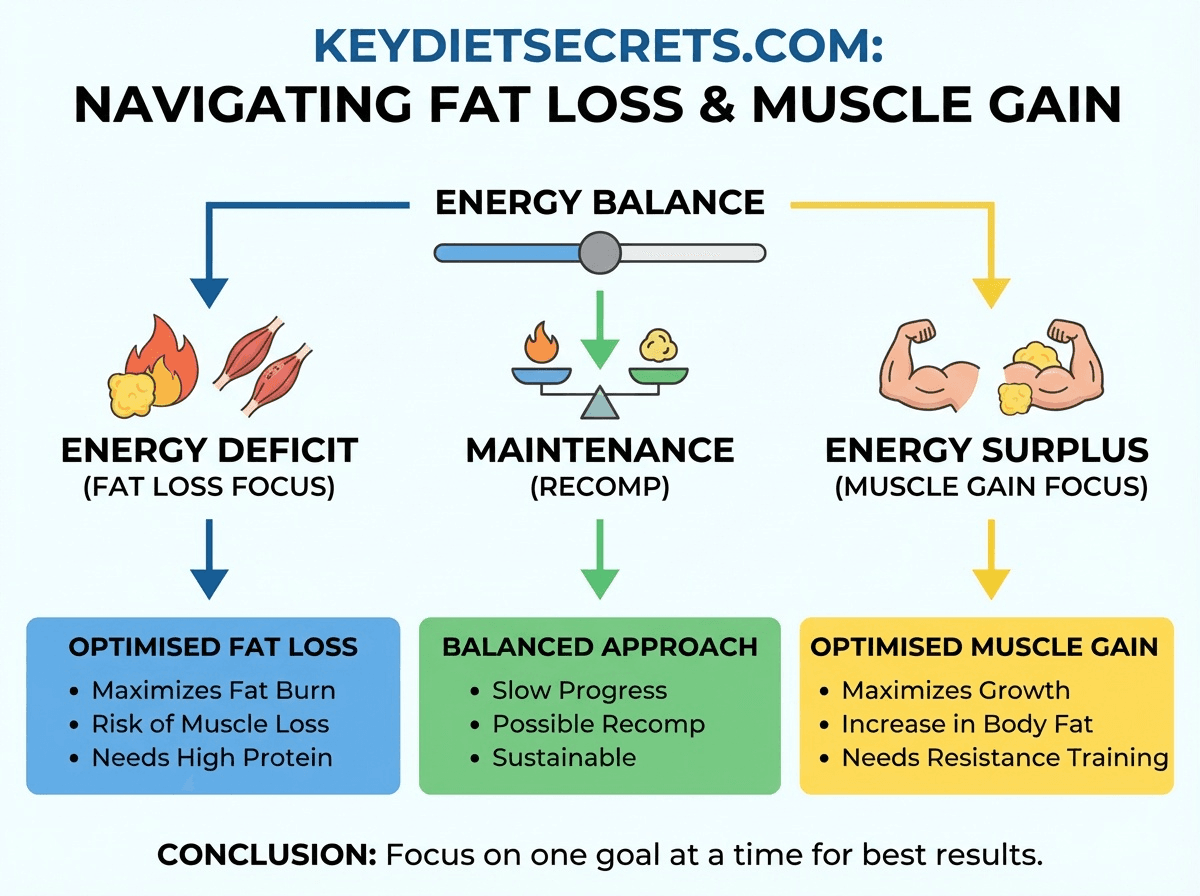
Why Adiponectin Matters for Weight Loss
Weight loss isn’t just about calories in vs. calories out.
It’s about:
- How easily your body accesses stored fat
- How stable your blood sugar and insulin responses are
- Whether your metabolism feels cooperative or resistant
Adiponectin plays a role in all three.
1. Adiponectin Improves Insulin Sensitivity
When adiponectin signaling is strong:
- Insulin works more efficiently
- Less insulin is needed to manage blood sugar
- Fat storage signals are reduced
This matters because chronically high insulin makes fat loss harder, even in a calorie deficit.
Lower adiponectin → higher insulin resistance → easier fat storage.
2. Adiponectin Helps Unlock Stored Fat
Adiponectin activates pathways involved in fatty-acid oxidation — essentially helping your body access stored fat for fuel.
When adiponectin is low:
- Fat loss feels “stuck”
- Energy dips are common
- Hunger signals can feel louder and less predictable
This is why supporting adiponectin can make fat loss feel less forced and more natural.
3. Adiponectin Reduces Inflammation That Blocks Progress
Chronic low-grade inflammation interferes with:
- Fat metabolism
- Muscle recovery
- Hormonal balance
Adiponectin has anti-inflammatory effects, which helps create a metabolic environment where fat loss can occur without excessive stress on the body.
What About Muscle Growth and Preservation?
This is where adiponectin becomes especially important for healthy weight loss.
Fat Loss vs. Weight Loss
Not all weight loss is good.
Rapid or poorly supported weight loss often leads to:
- Muscle loss
- Slower metabolism
- Rebound weight gain
Adiponectin supports fat loss over muscle loss indirectly by:
- Improving insulin sensitivity (important for muscle protein synthesis)
- Reducing inflammation (improves recovery)
- Supporting metabolic flexibility (switching between carbs and fat)
While adiponectin doesn’t “build muscle” directly, it creates conditions where muscle is easier to maintain and grow, especially when paired with:
- Adequate protein
- Resistance training
- Sufficient recovery
The Visceral Fat → Adiponectin Cycle
Visceral fat (fat stored deep around organs) is especially disruptive.
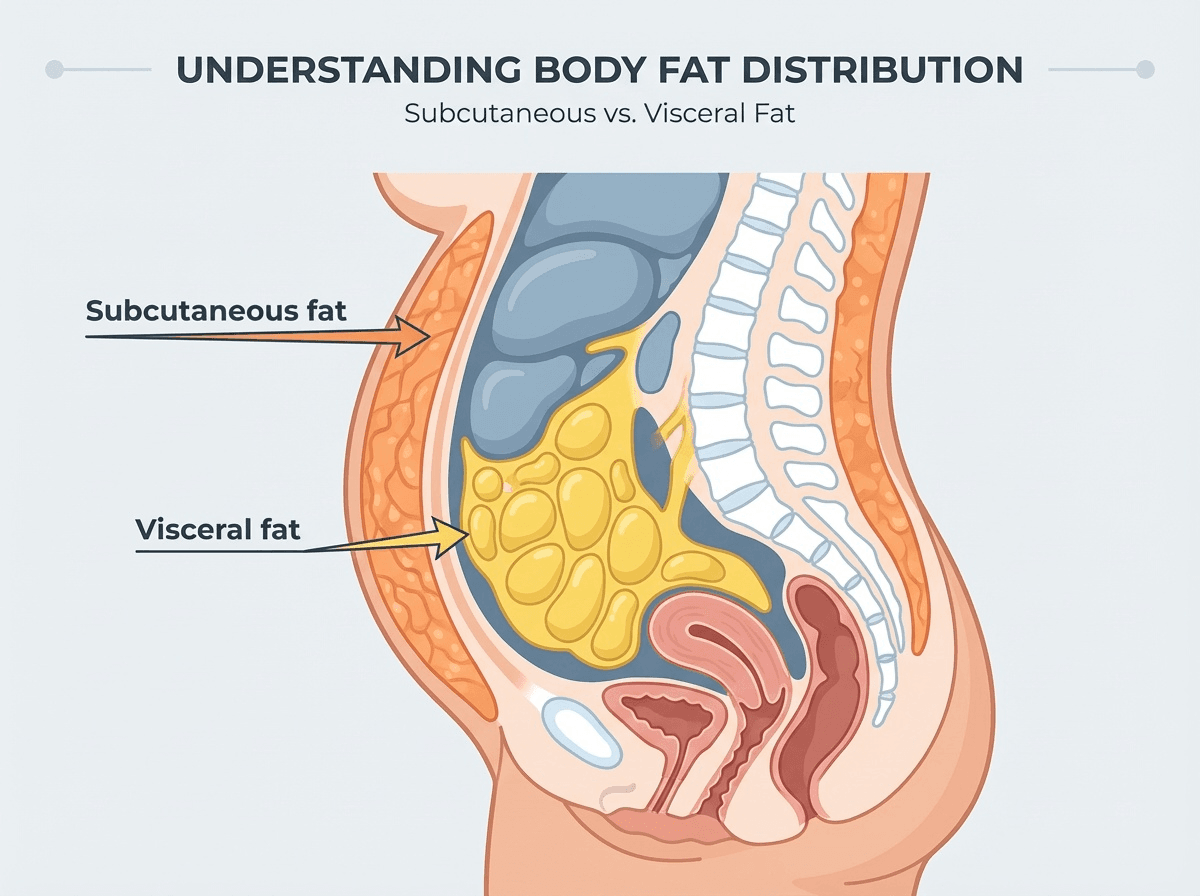
As visceral fat increases:
- Inflammatory signals increase
- Insulin resistance rises
- Adiponectin signaling declines
As adiponectin declines:
- Fat loss becomes harder
- Blood sugar regulation worsens
- More visceral fat tends to accumulate
This is why where fat is stored matters more than body weight alone.
The good news?
This cycle can be reversed — often with surprisingly modest changes.
How to Support Healthy Adiponectin (Practically)
You don’t “boost” adiponectin with hacks.
You create the conditions where it functions well.
1. Eat to Stabilize Blood Sugar (Not Spike It)
Meals that repeatedly spike blood sugar and insulin tend to suppress adiponectin signaling over time.
Build meals this way:
- Protein first (eggs, fish, poultry, Greek yogurt, tofu)
- Fiber next (vegetables, legumes, berries)
- Healthy fats (olive oil, nuts, seeds, avocado)
Avoid eating refined carbs alone. Pair them with protein and fat.
2. Prioritize Protein (Especially During Weight Loss)
Adequate protein helps:
- Preserve lean muscle
- Improve satiety
- Reduce overeating driven by blood sugar swings
General guideline:
Aim for protein at every meal, especially breakfast.
This supports insulin sensitivity — which supports adiponectin signaling.

3. Include Omega-3-Rich Foods Regularly
Omega-3 fats are associated with improved metabolic signaling.
Good sources:
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Trout
- Chia seeds
- Flax seeds
You don’t need megadoses — consistency matters more than quantity.
4. Avoid Extreme Calorie Restriction
Severe dieting increases stress hormones and inflammation — both of which work against adiponectin.
Signs your deficit is too aggressive:
- Constant fatigue
- Poor sleep
- Loss of strength
- Increased cravings
Safer fat loss supports hormones first, scale second.
5. Move Your Body (Without Overdoing It)
Exercise improves adiponectin signaling — even without weight loss.
Best options:
- Brisk walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Light-to-moderate resistance training
Consistency beats intensity.
You don’t need punishment workouts to improve metabolic health.
Can You Test Adiponectin?
Yes — adiponectin can be measured via blood tests, though it’s not part of standard panels.
If tested, interpretation should be done with a clinician, especially because:
- Higher isn’t always better in advanced disease states
- Context matters more than a single number
For most people, lifestyle signals (energy, hunger, body composition, blood sugar trends) matter more than lab optimization.
The Big Takeaway
Adiponectin helps explain why:
- Sustainable weight loss feels different than crash dieting
- Fat loss improves when metabolism is supported, not punished
- Muscle preservation depends on hormonal health, not just workouts
You don’t need to chase adiponectin directly.
You need to:
- Eat in ways that stabilize blood sugar
- Preserve muscle while losing fat
- Reduce inflammation and metabolic stress
Do that consistently — and adiponectin tends to take care of itself.